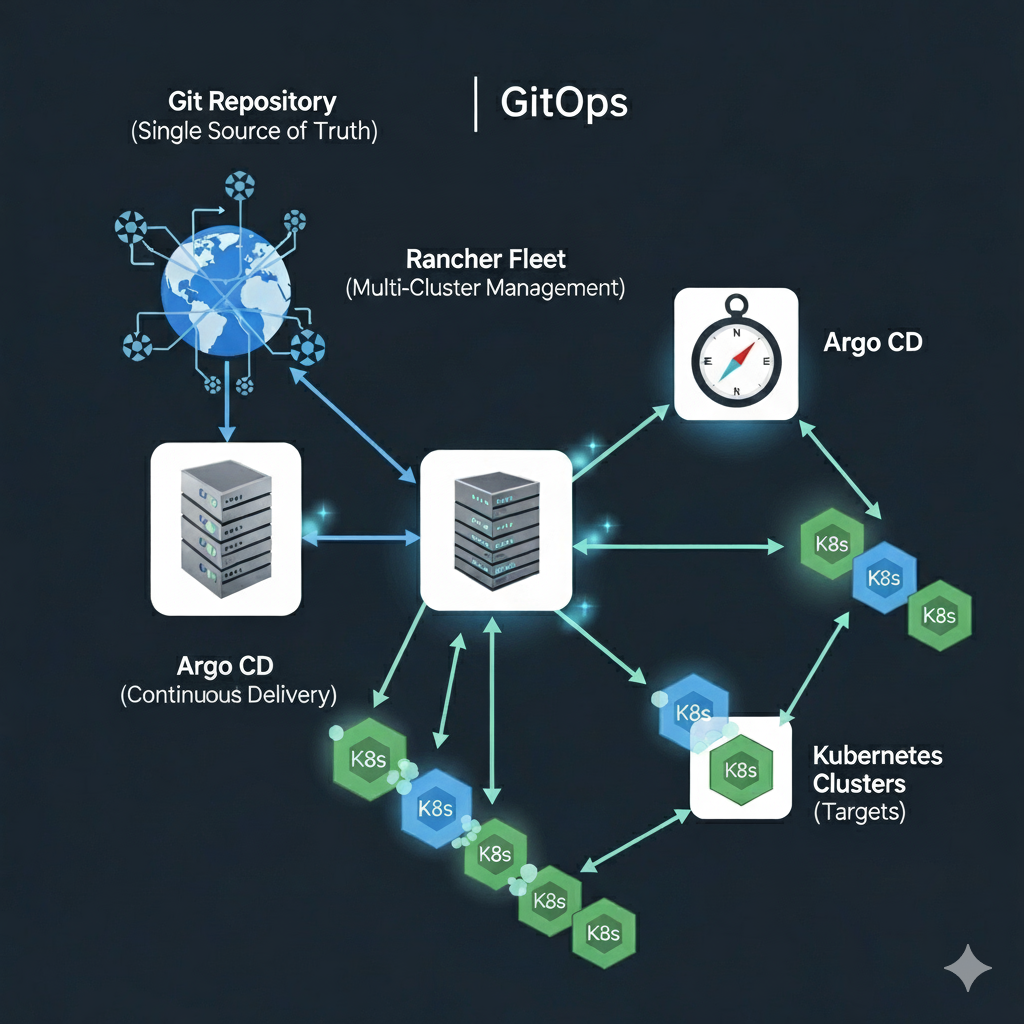
Part 2: Building a GitOps Pipeline with Rancher Fleet and Argo – From Code to Deployment
Recap of Part 1
In the first part of this series, we introduced GitOps, discussed its benefits, and set up a basic environment using Rancher Fleet. Now, we’ll take the next step by building a GitOps pipeline that automates your deployments from code commit to production, using Argo as our continuous integration (CI) tool and Fleet as the continuous deployment (CD) tool.
Designing a GitOps Pipeline with Rancher Fleet and Argo
Pipeline Components
A GitOps pipeline with Rancher Fleet and Argo involves several key stages:
- Code Commit: Developers commit changes to the Git repository.
- CI/CD Pipeline: Argo Workflow orchestrates the CI process, including testing, building, and deploying the application.
- GitOps Deployment: Fleet automatically picks up changes from the Git repository and applies them to the Kubernetes cluster.
- Monitoring: Tools like Prometheus and Grafana monitor the deployment, and any issues trigger alerts.
Diagram: GitOps Pipeline Flow with Argo
A flowchart showing each stage of the pipeline from code commit to deployment and monitoring, integrating Argo Workflows with Rancher Fleet.
Implementing the Pipeline
Step 1: CI/CD Integration with Argo
Set Up Argo Workflows for CI:
Argo Workflows is a Kubernetes-native workflow engine that enables you to define and execute complex workflows, such as CI pipelines.
Install Argo Workflows in your Kubernetes cluster:
First create a namespace:
kubectl create namespace argoFind the best release using the upgrade guide, update and apply the manifest for the version you wish to use.
kubectl apply -n argo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-workflows/3.7.1/manifests/install.yamlCreate a Workflow template to build and test your application. Here’s an example of a simple workflow:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Workflow
metadata:
generateName: ci-pipeline-
spec:
entrypoint: build-and-test
templates:
- name: build-and-test
steps:
- - name: build
template: build
- - name: test
template: test
- name: build
container:
image: golang:1.16
command: [bash, -c]
args: ["go build -o /app/myapp ."]
- name: test
container:
image: golang:1.16
command: [bash, -c]
args: ["go test ./..."]
This workflow builds and tests a Go application. You can customize it for your specific application stack.
Update Kubernetes Manifests in Git:
After a successful build and test, Argo can trigger an update to the Kubernetes manifests in the Git repository. This can be done by pushing a new commit to the repository with the updated image tag: yaml containers:
containers:
- name: my-app
image: my-registry/my-app:{{workflow.parameters.image-tag}}
Step 2: Deployment Automation with Fleet
Configure Fleet for Continuous Deployment:
Ensure Fleet is monitoring the correct branch and path in the Git repository.
Define a GitRepo resource that specifies where Fleet should look for changes:
apiVersion: fleet.cattle.io/v1alpha1
kind: GitRepo
metadata:
name: my-app-repo
namespace: fleet-default
spec:
repo: "https://github.com/myorg/my-app-repo.git"
branch: "main"
paths:
- "clusters/dev"
Apply Changes to the Cluster:
Once changes are pushed to the Git repository, Rancher Fleet will automatically detect the updates and deploy the new version to the Kubernetes cluster.
Step 3: Monitoring and Rollback
Set Up Monitoring with Prometheus and Grafana:
Deploy Prometheus and Grafana in your Kubernetes cluster to monitor the health of your applications.
Configure alerts in Prometheus to notify you if any deployments fail or if there are performance issues.
Automated Rollback:
Fleet provides rollback functionality, allowing you to automatically revert to a previous version if a deployment fails:
apiVersion: fleet.cattle.io/v1alpha1
kind: GitRepo
metadata:
name: my-app-repo
namespace: fleet-default
spec:
repo: "https://github.com/myorg/my-app-repo.git"
branch: "main"
paths:
- "clusters/dev"
rollback:
onFailure: true
Diagram: CI/CD and GitOps Integration with Argo and Rancher Fleet
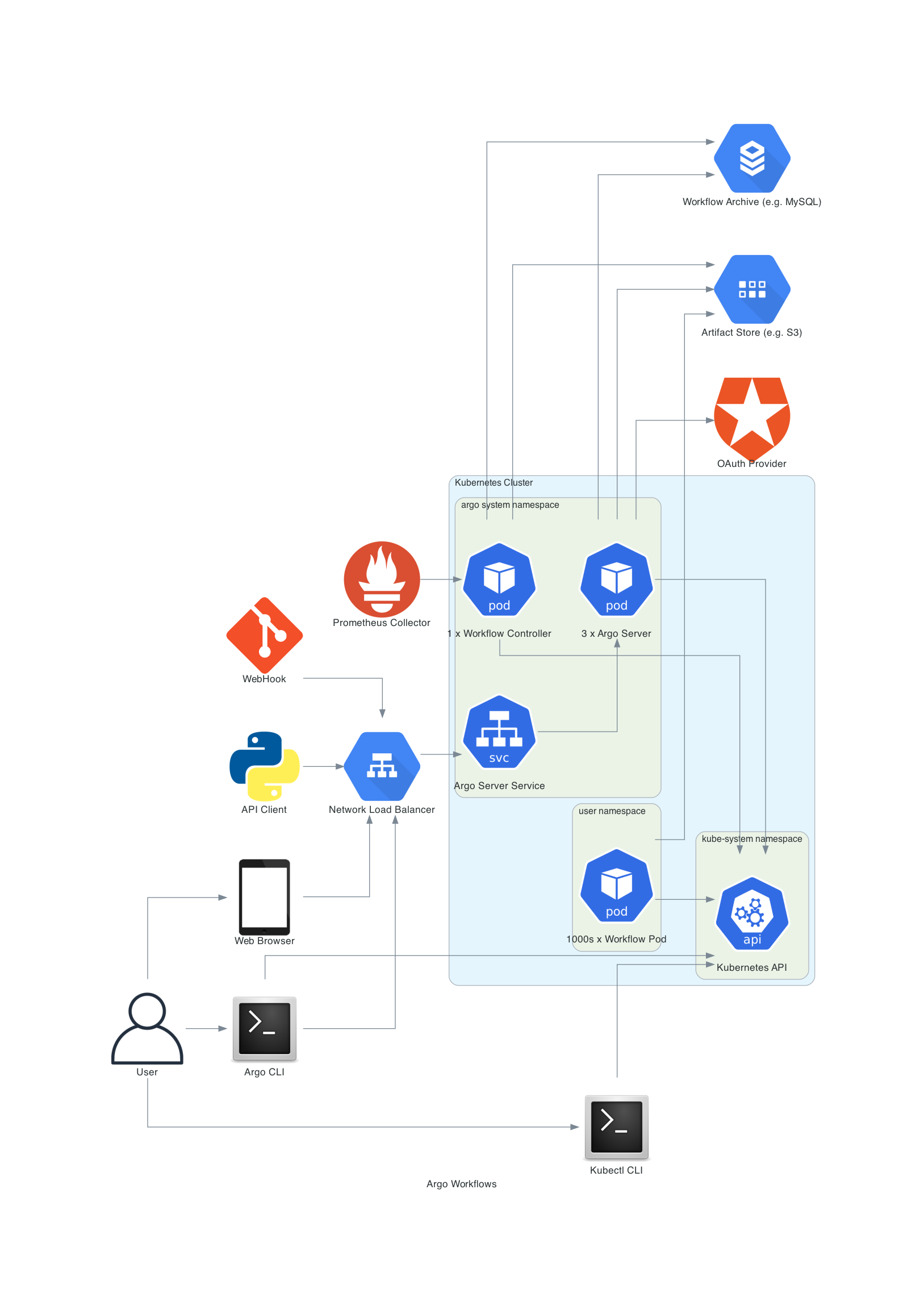
Real-World Example: Deploying a Kubernetes Application with GitOps
Step-by-Step Deployment
Code Push:
- Developer pushes code to the Git repository. This triggers an Argo Workflow.
CI Pipeline with Argo:
- Argo Workflow runs the build and test steps, then updates the Kubernetes manifests with the new image tag.
Fleet Deployment:
- Fleet detects changes in the Git repository and deploys the new version to the Kubernetes cluster.
Code Snippets and YAML Examples
- Argo Workflow: Define your build and deployment workflow in Argo, including steps to build, test, and push changes to the Git repository.
- Fleet Configuration: Example
GitReporesource configuration to ensure Fleet automatically deploys updates from Git.
Best Practices
Security Considerations
- RBAC in Argo: Use Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in Argo to restrict who can execute workflows and manage resources.
- Secret Management: Manage secrets securely using Kubernetes Secrets, Sealed Secrets, or external tools like HashiCorp Vault, and ensure they are properly integrated into your Argo workflows.
Optimization Tips
- Argo Workflow Efficiency: Optimize your Argo workflows by parallelizing steps where possible and using caching mechanisms to speed up builds.
- Fleet Resource Management: Ensure that Fleet’s resource management is configured to handle large deployments efficiently, especially in multi-cluster setups.
Wrap it up
In this part, we’ve walked through the process of building a GitOps pipeline using Rancher Fleet and Argo. This combination provides a powerful, scalable solution for automating your CI/CD processes and ensuring consistent, reliable deployments. In the next part of the series, we’ll focus on scaling GitOps practices to manage large environments and multiple Kubernetes clusters.
This post provides a comprehensive guide for integrating Argo with Rancher Fleet to create an automated, scalable GitOps pipeline. This approach is well-suited for managing complex, multi-environment Kubernetes deployments, ensuring that your infrastructure and applications are deployed consistently and reliably.